Content Index Administration
The content index, also called the search index, supports Confluence's search functionality. It is also used for a number of related functions such as building email threads in the mail archive, the space activity feature, and lists of recently-updated content. The Gliffy plugin also uses the index for some of its functionality.
For reasons of efficiency, Confluence does not immediately add content to the index. New and modified Confluence content is first placed in a queue and the queue is processed once every five seconds (by default).
Viewing the content index summary
To see information about your Confluence site's content indexing:
- Choose the cog icon , then choose General Configuration under Confluence Administration
- Choose 'Content Indexing' under the heading 'Administration' in the left-hand panel.
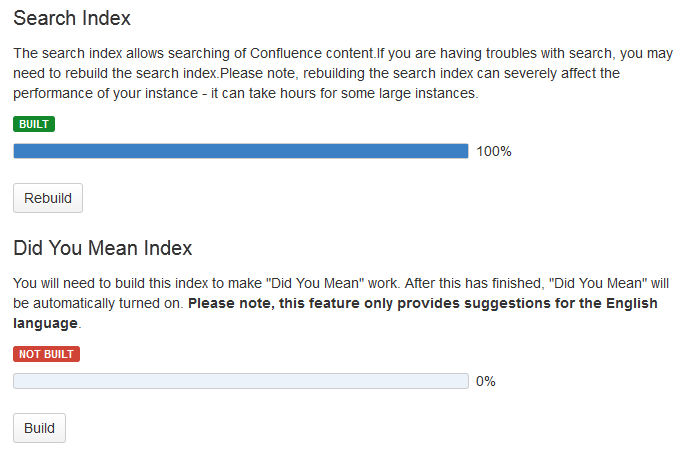
Screenshot: Index summary
Rebuilding the search index
The search index is maintained automatically, but you may need to rebuild it manually under circumstances such as these:
- Your searching and mail threading are malfunctioning.
- After an upgrade. If a re-index is required after an upgrade, it will be noted in an upgrade subsection of the relevant Confluence Release Notes.
To rebuild the search index:
- Choose the cog icon , then choose General Configuration under Confluence Administration
- Choose 'Content Indexing' under the heading 'Administration' in the left-hand panel.
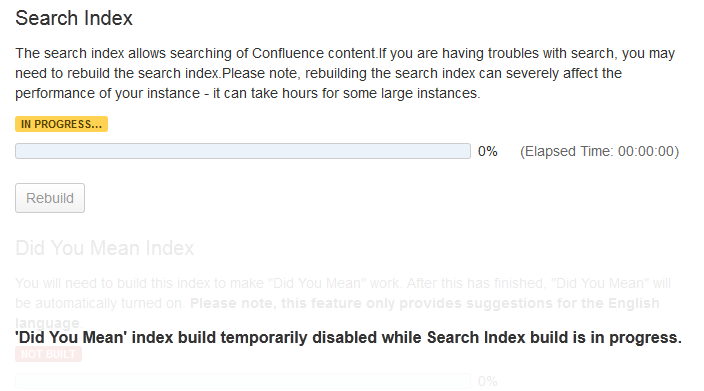
- Choose the 'Rebuild' button in either the 'Search Index' section.
(If the indexes has never been built, its button will indicate 'Build' instead of 'Rebuild.)
Screenshot: Content indexing
The 'Did You Mean' index is no longer relevant
The 'Did You Mean' feature is no longer available in Confluence. This index is therefore redundant, and will be removed at some time in the future.
Slow reindexing
Does the reindexing take a long time to complete? The length of time depends on the following factors:
- Number of pages in your Confluence instance.
- Number, type and size of attachments.
- Amount of memory allocated to Confluence.
- Disk throughput.
It may help to increase the heap memory allocation of Confluence by following the instructions here Increasing JIRA application memory. The process is basically the same for Confluence or JIRA applications.
If you are running an older version of Confluence and find that the index rebuild is not progressing, you may need to shut down Confluence, and restart it with the following Java system property set: bucket.indexing.threads.fixed=1. This will cause the re-indexing to happen in a single thread and be much more stable (but slower).
Viewing the index browser
Confluence uses a search engine called Lucene. If you need to see more details of the indexed pages in your Confluence site, you can download and run Luke. Luke is a development and diagnostic tool that accesses existing Lucene indexes and allows you to display and modify their content in several ways.
Start Luke and use it to open the index directory, located in your Confluence Home directory. For example:
c:\confluence\data\confluence-home\index.
Note: Confluence 5.2 (and later) use Lucene 4.3 (or later). If the Luke library has not been updated to support the latest version of Lucene, you can compile Luke yourself, from the fork on Github – please read the warnings and notes in the README file of that repository.
More hints and tips
- If you are still experiencing problems after performing the above rebuild, the next step might be to remove the index and rebuild it from scratch.
The space activity feature uses the index to store data. If you remove the index file, the existing activity data will disappear.
- A tip for the development community: If you have the Confluence source, you can look for references to the SmartListManager to find the screens and lists that rely on the content index.