Connecting Bitbucket Server to Oracle
This page describes how to connect Bitbucket Server to a Oracle database.
The overall process for using a Oracle database with Bitbucket Server is:
- Install Oracle where it is accessible to Bitbucket Server.
- Create a database and user on the Oracle server for Bitbucket Server to use.
- Install Bitbucket Server on Windows, or on Linux or Mac. See Getting started.
- Either:
- at Bitbucket Server install time, run the Setup Wizard to connect Bitbucket Server to the Oracle database, or
- at a later time, migrate Bitbucket Server to the Oracle database. See Using the Database Migration Wizard.
It is assumed here that you already have Oracle installed and running. For information about installing Oracle and creating Oracle databases, see the Oracle documentation pages. For the versions of Oracle supported by Bitbucket Server see Supported platforms.
Prerequisites
Backup
If you are migrating your data from the internal Bitbucket Server database, back up the Bitbucket Server home directory.
If you are migrating your Bitbucket Server data from a different external database, back up that database by following the instructions provided by the database vendor before proceeding with these instructions.
See Data recovery and backups.
Create the Bitbucket Server database
Before you can use Bitbucket Server with Oracle, you must set up Oracle as follows:
- Ensure that you have a database instance available for Bitbucket Server (either create a new one or use an existing one)
The character set of the database must be set to eitherAL32UTF8orUTF8, to support storage of Unicode data as per the Oracle documentation.
Note that it is important to the proper operation of Bitbucket Server that the database store its data in a case-sensitive manner. By changing the values of the NLS_COMP and/or NLS_SORT variables, it is possible to cause Oracle to perform its searches in a case-insensitive manner. We therefore strongly recommend that those variables be left at their default values. - Create a user that Bitbucket Server will connect as (e.g.
bitbucket).
Remember the database user name; it will be used to configure Bitbucket Server's connection to the database in subsequent steps.
When you create a user in Oracle, a schema is automatically created.
It is strongly recommended that you create a new database user for use by Bitbucket Server rather than sharing one that is used by other applications or people. - Grant the Bitbucket Server user
connectandresourceroles only. Theconnectrole is required to set up a connection, whileresourcerole is required to allow the user to create objects in its own schema. - Create a local
all_objectsview to the user's schema, so that there is no possibility that a table with the same name as one of the Bitbucket Server tables in another schema will cause any conflicts. - Note that Bitbucket Server requires the database to keep idle connections alive for at least 10 minutes. If the database is configured with less than a 10 minute connection timeout, there will be seemingly random connection errors.
The format of the command to create a user in Oracle is:
CREATE USER <user>
IDENTIFIED BY <password>
DEFAULT TABLESPACE USERS
QUOTA UNLIMITED ON USERS;
GRANT CONNECT, RESOURCE to <user>;
CREATE VIEW <user>.all_objects AS
SELECT *
FROM sys.all_objects
WHERE owner = upper('<user>');Here is a simple example, using SQL*Plus, of how one might create a user called bitbucket with password jdHyd6Sn21 in tablespace users, and grant the user a minimal set of privileges. When you run the command on your machine, remember to replace the username, password and tablespace names with your own values.
CREATE USER bitbucket
IDENTIFIED BY jdHyd6Sn21
DEFAULT TABLESPACE USERS
QUOTA UNLIMITED ON USERS;
GRANT CONNECT, RESOURCE to bitbucket;
CREATE VIEW bitbucket.all_objects AS
SELECT *
FROM sys.all_objects
WHERE owner = upper('bitbucket');This creates an empty Oracle schema with the name bitbucket, and a user that can log in from the host that Bitbucket Server is running on and who has full access to the newly created schema. In particular, the user is allowed to create sessions and tables.
Bitbucket Server will generally require about 25–30 connections to the database. The maximum number of connections is a configurable system property – see Database pool.
Connect Bitbucket Server to the Oracle database
You can now connect Bitbucket Server to the Oracle database, either:
- when you run the Setup Wizard, at install time,
- when you wish to migrate to Oracle, either from the embedded Bitbucket Server database or from another external database.
When running the Setup Wizard at install time
- Select External at the 'Database' step.
- Select Oracle for Database Type.
- Complete the form. See the table below for details.
- Click Next, and follow the instructions in the Bitbucket Server Setup Wizard.
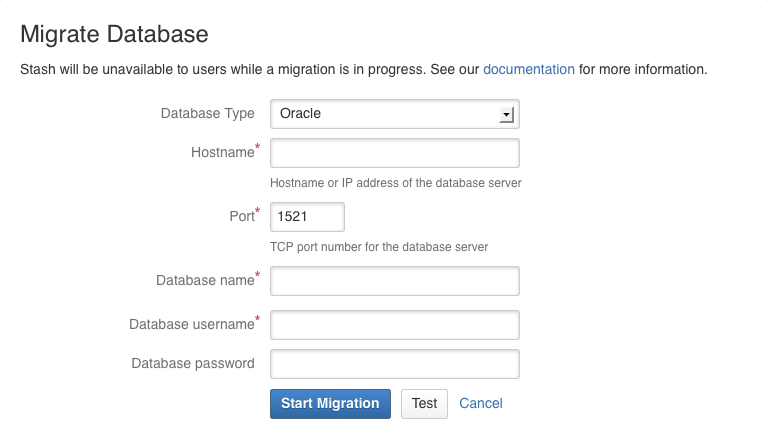
When migrating to Oracle
- In the Bitbucket Server administration area, click Database (under 'Settings').
- Click Migrate database.
- Select Oracle for Database Type.
- Complete the form. See the table below for details.
- Click Start Migration.
Hostname
The hostname or IP address of the computer running the database server.
Port
The TCP port with which Bitbucket Server can connect to the database server. The default value is the default port that MySQL or MariaDB runs against. You can change that if you know the port that your MySQL or MariaDB instance is using.
Database name
The name of the database that Bitbucket Server should connect to.
Database username
The username that Bitbucket Server should use to access the database.
Database password
The password that Bitbucket Server should use to access the database.